An economic entity needs to portray its financial information to all the stakeholders. All the financial statements and the information must be true and should represent the picture of the entity.
Implementing an appropriate financial system demands a complete understanding of economic status and maintaining uniformity in the accounting process. The golden rules of accounting help you enjoy this uniformity and account for all the transactions correctly.
By building the foundation of passing journal entries, these accounting rules form the soul of accounting and bookkeeping. Let’s understand the three golden accounting rules that help to eliminate the complicated process of recording your company’s financial transactions.
Table of Contents
Why Accounting for Your Business?
Every business regardless of the operation, complexity, and size needs to deal with accounting. With the increased evolution of modern-day business, business processes, and accounting go hand in hand, which means they can’t function without relying on each other.
Recording the financial transactions through accounting helps to improve business performance through the preparation of financial statements. Internal and external stakeholders such as tax authorities, investors, banks, regulators, and other users utilise these financial statements.
Accounting Principles – An Overview
Accounting principles state the standard rules and regulations required to record financial transactions and generate financial statements. Accounting principles are the basic guidelines useful to record and prepare financial statements.
Basic Accounting Principles
There are certain accounting principles you need to keep in mind while making financial statements. Let’s take a glance at these basic accounting principles:
- Revenue Recognition (Accrual Accounting) Principle
Any accounting transaction needs to be reported as soon as it occurs without waiting for the cash flow to be received from the transaction. In this principle, receipts, and payments get recorded as they are accrued and not at the time of realisation.
- Cash/ Mercantile System of Accounting
Transactions in this method are noted as and when they are debited and credited. This principle requires businesses to keep track of the goods purchased, services offered, or the capital assets acquired without adjusting them for the changes in the market value of the assets.
GAAP and its Principles
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, or GAAP, form a compilation of rules, procedures, and standards implemented and revised by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB).
The key focus of GAAP is to ensure the consistency, completeness, and comparability of the company’s financial statements. It enables investors to easily analyse and extract significant information from the financial statements, which incorporates the data trends of a specific duration.
Let’s take a look at the 10 GAAP principles listed below:
- Principle of Regularity: GAAP-compliant experts strongly adhere to the well-laid rules and regulations.
- Principle of Consistency: Standards are implemented throughout the financial reporting with consistency.
- Principle of Sincerity: GAAP-compliant accountants follow a commitment to accuracy and impartiality.
- Principle of Permanence of Methods: Consistent steps are leveraged in preparing financial reports.
- Principle of Non-Compensation: Without a prospect of debt compensation, both positive and negative aspects that contribute to the performance of an organisation is reported completely.
- Principle of Prudence: Speculation doesn’t influence the financial data reporting.
- Principle of Continuity: Evaluation of assets assumes the organisation’s operations shall continue.
- Principle of Periodicity: Reporting revenues is divided by standard accounting periods like fiscal years.
- Principle of Materiality: Financial reports should reveal the monetary situation of a business.
- Principle of Utmost Good Faith: Every party involved is assumed to act honestly.
Journal Entries in Accounting
Journal entries are the pillar stones of accounting, which focuses on serving a comprehensive documentation of every business activity involved. It makes sure that no transaction goes unrecorded or unnoticed. By following the double-entry bookkeeping principles, journal entries maintain a balance between debits and credits, to make accurate financial statements.
- Assets
Asset refers to the things a company owns and has economic value, which could be sold out for money, such as equipment, cash, real estate, and automobiles.
- Liabilities
The amounts owed by the company to either an individual or an entity, such as the accounts payable or loans.
- Expenses
Expenses define the charges for salaries, materials, and related operational costs incurred during the business processes.
- Income and revenue
These terms relate to the money earned from sales, services, or other such commercial endeavours.
What is the Accounting Equation?
The accounting equation is represented as follows:
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
Capital is the residual interest in the business’s assets after eliminating all the liabilities. While considering a limited liability company, capital is termed as an ‘equity’. Capital represents how much the owners invest in the business with retained profits or losses.
Assets (Dr)= Capital (Cr) + Liabilities (Cr)
Which means that the sum of debits equals the sum of credits. Debits and credits build a foundation for accounting. Debits and credits act as the driving force in the accounting industry.
A thorough know-how of the complexities that pertain to debits and credits is inevitable to understand the golden rules of accounting.
Here’s how debits and credits impact the four types of accounts:
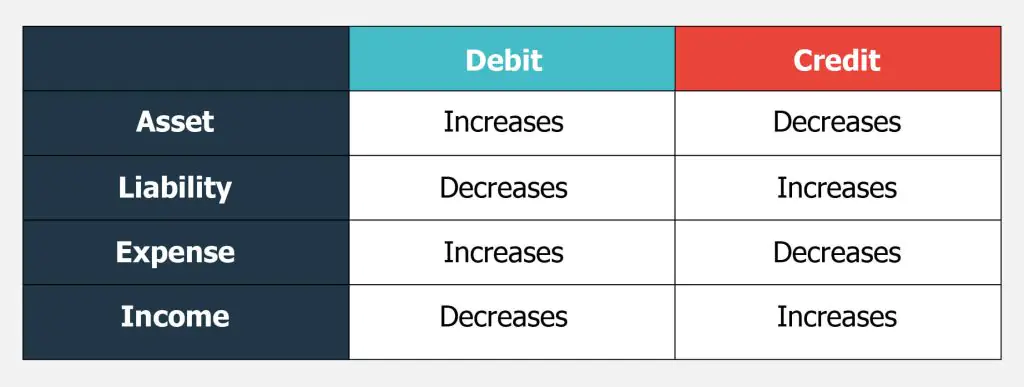
Three Types of Accounts
In financial accounting, each debit or credit transaction entry belongs to any of the three types of accounts as listed below:
1. Nominal Account
A nominal account is a general ledger that includes business transactions such as profits, losses, incomes, and expenses. It encompasses all transactions that take place in a fiscal year. Additionally, it resets to zero and restarts the following fiscal year. The commission received, rent account, salary account, and interest account are all examples of a nominal account.
2. Personal Account
It is a general ledger that relates to associations, people, or businesses. Furthermore, it is categorised into three subcategories, namely:
- Artificial personal account
Artificial personal account signifies bodies other than human beings, however, form separate legal entities based on the law. For instance, hospitals, government bodies, companies, banks, partnerships, cooperatives, etc.
- Natural personal account
Natural personal account refers to human beings; this could be a drawings account, capital account, debtor, creditor, etc.
- Representative personal account
This personal account highlights the accounts of natural or artificial entities. But, the transactions of this type of account either fall on the previous year or the year that follows. For instance, a representative personal account includes the information on the due salary of the employee from last year. Also, it could represent the rent expense a company paid in advance for the next year.
3. Real account
Like the previous two, a real account is a general ledger, however, it includes transactions specific to the assets and liabilities of a firm. The assets in this case can be classified into two, namely: tangible and intangible assets.
Tangible assets encompass land, machinery, buildings, furniture, etc. The intangible assets include patents, goodwill, copyrights, etc. A real account doesn’t close after a financial year is completed. Instead, it gets carried forward to the subsequent year. Additionally, real accounts are also visible in the company’s balance sheet.
As you’re now familiar with the types of accounts, let’s dive into the golden rules of accounting:

First Rule: “Debit the receiver and credit the giver”
A personal account, i.e., a general ledger account linked to the defined people or entities is subject to this rule of accounting. For a personal account, it gets debited whenever you receive something. On the contrary, your account gets credited when you give something. Let’s consider a case that can help you understand the concept in detail:
Think of a scenario where you have purchased $500 worth of items from a company named ‘XYZ’. Here, you need to include two entries to your books as per the first rule. Firstly, you need to give credit to your company since they provide the items for your firm. Secondly, you should debit your purchase account being the recipient.
| Date | Account | Debit | Credit |
| DD-MM-YYYY | Purchase | 500 | |
| Accounts Payable | 500 |
Second Rule: “Debit what comes in and credit what goes out”
The second golden rule of accounting deals with permanent accounts also called real accounts, which don’t close when the accounting period ends. Real accounting encompasses assets, liabilities, and equity, and accounts for contra-assets, contra-equity, and contra-liabilities.
For real accounts, you need to debit the account whenever something enters your firm, as an asset. On the contrary, you should credit the account when you experience a decrease in assets— i.e., when something departs your business.
For example, say you paid $1000 cash for some furniture. You would make the following entries if you followed the second rule. Consider the rule that you should debit the furniture account for the incoming funds and credit the cash account to represent the outgoing funds.
| Date | Account | Debit | Credit |
| DD-MM-YYYY | Furniture | 1000 | |
| Cash | 1000 |
A credit entry to the cash account denotes the decline in cash since it leaves your company for purchase. However, a debit entry to the furniture account signifies the increased value of the furniture.
Third Rule: “Debit expenses and losses whereas credit incomes and gains”
The third rule of accounting covers the normal accounts, or the transient accounts which are mandatorily closed at the end of every accounting period. Revenue, gain and expenditure are all examples of nominal accounts.
While considering nominal accounts, you need to debit the account whenever your firm experiences an expense or a loss. However, you should credit the account when your company earns a profit or generates money. Let’s take an example that explains how the third rule of accounting can be applied.
Let’s say you invested $2000 on items from a firm ABC. According to the third golden rule, the entries must be accustomed to appropriately recording the transaction. To record the rise in expenses incurred, you would debit the $2000 purchase (expense account) and to record the subsequent decrease in the income, you need to credit the income account.
| Date | Account | Debit | Credit |
| DD-MM-YYYY | Purchase | 2000 | |
| Cash | 2000 |
Advantages Of The Golden Rules Of Accounting
Appropriate maintenance of business records
Proper maintenance of records plays a pivotal role in determining the company’s success. With record maintenance, you can ensure that they are stored safely and systematically.
Comparison of financial results
Golden accounting rules make sure that the financial results are properly recorded. This lets businesses compare the financial results year-over-year efficiently.
Detailed business valuation
When a company calculates its financial statements properly, it makes the business valuation well-defined. Furthermore, it makes getting more investments easier while expanding the business.
Helps in future estimates and budgeting
If your business has a sound budget based on the best accounting practices, it builds a strong pillar for growth. Additionally, it helps in gaining more projections.
Evidence for legal concerns
Recording financial information is highly recommended for prompt reference during lawsuits. With golden accounting rules, this becomes handy and systematic, serving as solid proof for legal purposes.
Assistance in tax-specific matters
Lack of proper accounting practices could lead to huge penalties. This also negatively impacts the brand value and image. Accounting a firm’s financial statements helps companies to prevent shortfalls in taxes.
Compliance with regulatory authorities
Accounting becomes most significant while considering compliance with regulatory authorities. Without a well-laid accounting discipline, it becomes hard for any firm to achieve regulatory compliance.
Now that you have a clear understanding of the idea of golden rules of accounting, you can recognise the account to which each type of transaction belongs. So, this helps journal entries on financial transactions to stay specific, legitimate, and accurate.
Outsource Accounting services to the top Accounting firm in Dubai
If you wish to outsource your accounting services in Dubai and the UAE, Kreston Menon has the expertise to provide the best accounting and bookkeeping services in Dubai and all over the UAE. With years of experience in this field, the company has supported many clients across various sectors with reliable accounting services.
The qualified accounting professionals and the use of advanced technologies have helped the team to offer the most in-demand accounting services in the UAE. Earmarked as one of the leading accounting firms in Dubai, Kreston Menon has a skilled team of accountants with ample expertise in handling the laws of the UAE and financial reporting standards to offer accounting and bookkeeping services in Dubai.
Wrapping Up
By the 3 Golden Rules of Accounting, we define something similar to the letters of the English alphabet. If you’re unfamiliar with the letters, you can’t put the words together, and cannot use the language. Likewise, for accounting, when you are unfamiliar with the golden accounting rules, you can’t pass journal entries and can’t account for the transactions accurately.
Golden rules of accounting offer systematic instructions to enable the recording of financial transactions to accountants. Accountants can analyze which accounts need to be credited and which need to be debited using the accounting rules, ensuring the completeness and accuracy of the business’s financial records. The best accounting services in Dubai offer the reliable assistance you expect to resolve all possible concerns specific to accounting effectively.

FAQ
- Why are accounting concepts important?
The generally set rules and regulations help in attaining reliability and uniformity, which cultivates a better understanding of the financial statements. Accounting concepts help in recording financial transactions, such as every phase to ensure a well-planned, organised, and crisp business model.
- What is debit and credit?
As per financial bookkeeping, debit means the incoming money and credit refers to the money that goes out from the business. For balancing the books, you need to have a proper credit record in the account for every debit. And both should present equal value.
- What is the accounting rule for journal entries?
Every journal entry should include a debit and credit side. Even if the amounts associated with debit and credit belong to different accounts, They should produce equal amounts in both columns of the journal entry.
- What is a cashbook in accounting?
The cashbook is a kind of financial journal, which keeps a record of every cash transaction within an organisation. It records a receipt and payments of money paid out and received in detail and all the transactions are arranged in chronological order.
- What are the advantages of accounting?
The key advantages of accounting include appropriate maintenance of business records, savings on cost and time, increased financial visibility, ideal preparation of financial statements, smooth decision-making, evidence in legal matters, efficiency in taxation, effective business valuation, etc.

